Introduction:
Introduction Goods and Services Tax (GST) is one of the most significant tax reforms in India’s history. Introduced on July 1, 2017, GST subsumed numerous indirect taxes and created a unified tax structure across the country. As we move into 2025, understanding GST has become essential for every consumer, business owner, and student of economics. In this comprehensive blog, we’ll break down everything about GST—its meaning, structure, types, benefits, registration process, returns, penalties, and recent updates.
BUY NOW:
1. What is GST?
GST is a destination-based indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. It is collected at each stage of the supply chain, but the credit of tax paid is available at the previous stage, ensuring no cascading effect.
Why GST?
- To unify the Indian market.
- To remove the cascading effect of taxes.
- To promote transparency and efficiency.
- To improve tax compliance.
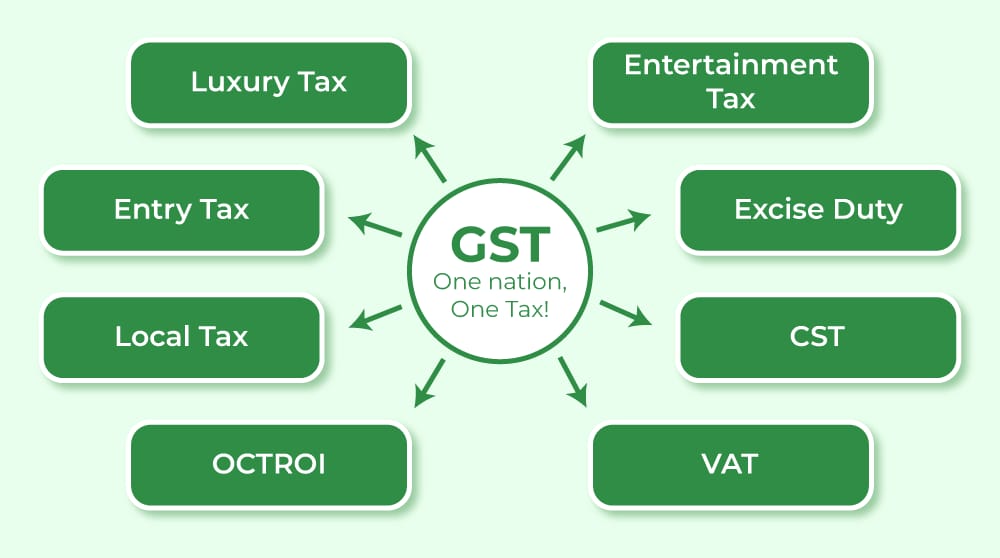
2. Taxes Replaced by GST
Before GST, India had multiple indirect taxes. GST subsumed taxes like:
- Central Excise Duty
- Service Tax
- VAT
- CST
- Octroi
- Entertainment Tax (except local bodies)
- Entry Tax, Purchase Tax, etc.
3. Types of GST:
GST is divided into four types:
a. CGST (Central GST)
- Levied by the central government on intra-state supply.
- Example: Sale within Gujarat, CGST + SGST applied.
b. SGST (State GST)
- Levied by the state government on intra-state supply.
- Revenue shared with state government.
c. IGST (Integrated GST)
- Levied by the central government on inter-state supply and imports.
- Revenue shared between center and state.
d. UTGST (Union Territory GST)
- Applicable to union territories like Delhi, Chandigarh, etc.
4. Structure of GST Rates:
GST has multiple tax slabs depending on the nature of goods/services:
- 0%: Essential items like fruits, vegetables, milk
- 5%: Basic necessities like packaged food, footwear
- 12%: Processed food, mobile phones
- 18%: Services, ACs, refrigerators
- 28%: Luxury items, cars, tobacco, aerated drinks
Special Category:
- Gold, rough diamonds – taxed at 3% and 0.25%
5. GST Registration:
Businesses must register for GST if:
- Annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakh (goods) or ₹20 lakh (services)
- Inter-state supply
- E-commerce seller
- Casual taxable person
Documents Required:
- PAN card
- Aadhaar card
- Business address proof
- Bank account details
Steps to Register:
1. Visit www.gst.gov.in
2. Fill Part-A and get TRN (Temporary Reference Number)
3. Fill Part-B with documents
4. ARN generated and certificate issued
6. GST Returns:
All registered taxpayers must file returns:
- GSTR-1: Monthly/quarterly sales return
- GSTR-3B: Monthly summary return
- GSTR-9: Annual return
Late Fees & Penalties:
- ₹50 per day (₹20 for nil returns)
- Interest @ 18% per annum
7. Input Tax Credit (ITC)
ITC allows you to reduce the tax paid on inputs from your output tax liability.
Conditions to claim ITC:
- Possession of a tax invoice
- Receipt of goods/services
- GST return filed by supplier
Blocked ITC:
- Personal use
- Goods lost or stolen
- Free samples, gifts

8. Composition Scheme
- For small taxpayers with turnover up to ₹1.5 crore (₹75 lakh in some states)
- Pay lower tax rate (1%-5%)
- No ITC available
- File quarterly returns (CMP-08)
9. GST on E-commerce
- E-commerce operators must deduct TCS @1%
- Sellers need to register under GST
- Returns like GSTR-8 to be filed
10. Benefits of GST
- Simplified tax structure
- Elimination of tax-on-tax
- Boost to Make in India
- Greater transparency
- Better compliance
- Easier interstate trade
11. GST Council
- Apex body for GST decisions
- Chaired by Union Finance Minister
- Members: State finance ministers
- Responsible for rate revisions, exemptions, procedural changes
12. Challenges in GST Implementation
- Technical glitches in GSTN
- Delays in refunds
- High compliance for small businesses
- Frequent rate changes
- Classification disputes
13. GST Audit
- Required if turnover exceeds ₹5 crore
- Audit by CA/CMA
- Reconciliation of returns with financial statements
14. E-Invoicing under GST
- Mandatory for businesses with turnover above ₹5 crore
- Invoice generated through IRP (Invoice Registration Portal)
- Enhances transparency and curbs fraud
15. Penalties under GST
- Wrong invoice: ₹25,000
- Non-registration: ₹10,000 or tax evaded, whichever is higher
- Fraudulent ITC claim: 100% penalty
- Wrong return: ₹100 per day
16. Recent Changes in GST (2024-25)
- Rate rationalization for online gaming
- New return filing system under trial
- Biometric-based Aadhaar authentication for registration
- Increased crackdown on fake ITC claims
17. GST for Exporters
- Exports are zero-rated
- ITC refund available
- LUT (Letter of Undertaking) required for tax-free export
18. GST Helpline & Assistance
- National helpline: 1800-103-4786
- Grievance Redressal Portal: selfservice.gstsystem.in
- Regional GST offices and Seva Kendras
19. Future of GST in India
- Introduction of single GST rate in the future
- Inclusion of petroleum and alcohol
- Full automation of compliance
- AI-based fraud detection
Conclusion:
GST is a revolutionary step that has simplified indirect taxation in India. With its continuous evolution, it is becoming more taxpayer-friendly. For businesses, understanding GST compliance is not only a legal obligation but also a growth enabler. Whether you’re a student, entrepreneur, or professional, this comprehensive guide empowers you to stay compliant, avoid penalties, and take advantage of every benefit that GST offers.
Note: All details in this blog are updated as of April 2025 and are subject to change based on government notifications.


